将 Props 传递给组件
React 组件使用 props 来互相通信。每个父组件都可以提供 props 给它的子组件,从而将一些信息传递给它。Props 可能会让你想起 HTML 属性,但你可以通过它们传递任何 JavaScript 值,包括对象、数组和函数。
You will learn
- 如何向组件传递 props
- 如何从组件读取 props
- 如何为 props 指定默认值
- 如何给组件传递 JSX
- Props 如何随时间变化
熟悉的 props
Props 是你传递给 JSX 标签的信息。例如,className、src、alt、width 和 height 便是一些可以传递给 <img> 的 props:
function Avatar() { return ( <img className="avatar" src="https://i.imgur.com/1bX5QH6.jpg" alt="Lin Lanying" width={100} height={100} /> ); } export default function Profile() { return ( <Avatar /> ); }
你可以传递给 <img> 标签的 props 是预定义的(ReactDOM 符合 HTML 标准)。但是你可以将任何 props 传递给 你自己的 组件,例如 <Avatar> ,以便自定义它们。 就像这样!
向组件传递 props
在这段代码中, Profile 组件没有向它的子组件 Avatar 传递任何 props :
export default function Profile() {
return (
<Avatar />
);
}你可以分两步给 Avatar 一些 props。
步骤 1: 将 props 传递给子组件
首先,将一些 props 传递给 Avatar。例如,让我们传递两个 props:person(一个对象)和 size(一个数字):
export default function Profile() {
return (
<Avatar
person={{ name: 'Lin Lanying', imageId: '1bX5QH6' }}
size={100}
/>
);
}如果
person=后面的双花括号让你感到困惑,请记住,在 JSX 花括号中,它们只是一个对象。
现在,你可以在 Avatar 组件中读取这些 props 了。
步骤 2: 在子组件中读取 props
你可以通过在 function Avatar 之后直接列出它们的名字 person, size 来读取这些 props。这些 props 在 ({ 和 }) 之间,并由逗号分隔。这样,你可以在 Avatar 的代码中使用它们,就像使用变量一样。
function Avatar({ person, size }) {
// 在这里 person 和 size 是可访问的
}向使用 person 和 size props 渲染的 Avatar 添加一些逻辑,你就完成了。
现在你可以配置 Avatar ,通过不同的 props,使它能以多种不同的方式进行渲染。尝试变换值吧!
import { getImageUrl } from './utils.js'; function Avatar({ person, size }) { return ( <img className="avatar" src={getImageUrl(person)} alt={person.name} width={size} height={size} /> ); } export default function Profile() { return ( <div> <Avatar size={100} person={{ name: 'Katsuko Saruhashi', imageId: 'YfeOqp2' }} /> <Avatar size={80} person={{ name: 'Aklilu Lemma', imageId: 'OKS67lh' }} /> <Avatar size={50} person={{ name: 'Lin Lanying', imageId: '1bX5QH6' }} /> </div> ); }
Props 使你独立思考父组件和子组件。 例如,你可以改变 Profile 中的 person 或 size props,而无需考虑 Avatar 如何使用它们。 同样,你可以改变 Avatar 使用这些 props 的方式,不必考虑 Profile。
你可以将 props 想象成可以调整的 “旋钮”。它们的作用与函数的参数相同 —— 事实上,props 正是 组件的唯一参数! React 组件函数接受一个参数,一个 props 对象:
function Avatar(props) {
let person = props.person;
let size = props.size;
// ...
}通常你不需要整个 props 对象,所以可以将它解构为单独的 props。
给 prop 指定一个默认值
如果你想在没有指定值的情况下给 prop 一个默认值,你可以通过在参数后面写 = 和默认值来进行解构:
function Avatar({ person, size = 100 }) {
// ...
}现在, 如果 <Avatar person={...} /> 渲染时没有 size prop, size 将被赋值为 100。
默认值仅在缺少 size prop 或 size={undefined} 时生效。 但是如果你传递了 size={null} 或 size={0},默认值将 不 被使用。
使用 JSX 展开语法传递 props
有时候,传递 props 会变得非常重复:
function Profile({ person, size, isSepia, thickBorder }) {
return (
<div className="card">
<Avatar
person={person}
size={size}
isSepia={isSepia}
thickBorder={thickBorder}
/>
</div>
);
}重复代码没有错(它可以更清晰)。但有时你可能会重视简洁。一些组件将它们所有的 props 转发给子组件,正如 Profile 转给 Avatar 那样。因为它们不直接使用它们任何 props,所以使用更简洁的 “展开” 语法是有意义的:
function Profile(props) {
return (
<div className="card">
<Avatar {...props} />
</div>
);
}这会将 Profile 的所有 props 转发到 Avatar,而不列出每个名字。
请克制地使用展开语法。 如果你在所有其他组件中都使用它,那就有问题了。 通常,它表示你应该拆分组件,并将子组件作为 JSX 传递。 接下来会详细介绍!
将 JSX 作为子组件传递
嵌套浏览器内置标签是很常见的:
<div>
<img />
</div>有时你会希望以相同的方式嵌套自己的组件:
<Card>
<Avatar />
</Card>当您将内容嵌套在 JSX 标签中时,父组件将在名为 children 的 prop 中接收到该内容。例如,下面的 Card 组件将接收一个被设为 <Avatar /> 的 children prop 并将其包裹在 div 中渲染:
import Avatar from './Avatar.js'; function Card({ children }) { return ( <div className="card"> {children} </div> ); } export default function Profile() { return ( <Card> <Avatar size={100} person={{ name: 'Katsuko Saruhashi', imageId: 'YfeOqp2' }} /> </Card> ); }
尝试用一些文本替换 <Card> 中的 <Avatar>,看看 Card 组件如何包裹任意嵌套内容。它不必 “知道” 其中渲染的内容。你会在很多地方看到这种灵活的模式。
您可以将带有 children prop 的组件看作有一个 “洞”,可以由其父组件使用任意 JSX 来 “填充”。你会经常使用 children prop 来进行视觉包装:面板、网格等等。
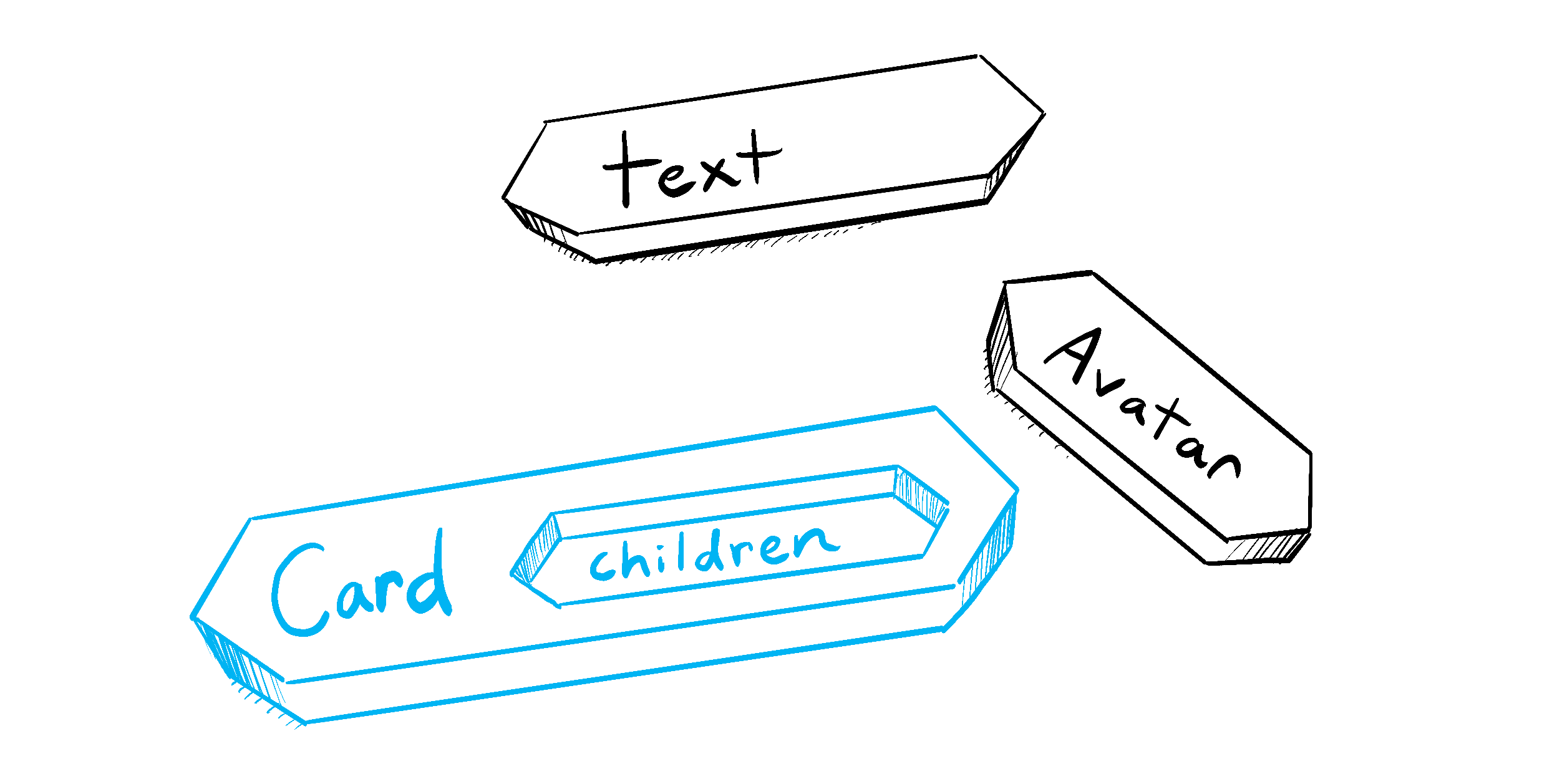
Illustrated by Rachel Lee Nabors
Props 如何随时间变化
下面的 Clock 组件从其父组件接收两个 props:color 和 time。(父组件的代码被省略,因为它使用 state,我们暂时不会深入研究。)
尝试在下面的选择框中更改颜色:
export default function Clock({ color, time }) { return ( <h1 style={{ color: color }}> {time} </h1> ); }
这个例子说明,一个组件可能会随着时间的推移收到不同的 props。 Props 并不总是静态的!在这里,time prop 每秒都在变化。当你选择另一种颜色时,color prop 也改变了。Props 反映了组件在任何时间点的数据,并不仅仅是在开始时。
然而,props 是 不可变的(一个计算机科学术语,意思是 “不可改变”)。当一个组件需要改变它的 props(例如,响应用户交互或新数据)时,它不得不 “请求” 它的父组件传递 不同的 props —— 一个新对象!它的旧 props 将被丢弃,最终 JavaScript 引擎将回收它们占用的内存。
不要尝试 “更改 props”。 当你需要响应用户输入(例如更改所选颜色)时,你可以 “设置 state”,你可以在 State: 一个组件的内存 中继续了解。
Recap
- 要传递 props,请将它们添加到 JSX,就像使用 HTML 属性一样。
- 要读取 props,请使用
function Avatar({ person, size })解构语法。 - 你可以指定一个默认值,如
size = 100,用于缺少值或值为undefined的 props 。 - 你可以使用
<Avatar {...props} />JSX 展开语法转发所有 props,但不要过度使用它! - 像
<Card><Avatar /></Card>这样的嵌套 JSX,将被视为Card组件的childrenprop。 - Props 是只读的时间快照:每次渲染都会收到新版本的 props。
- 你不能改变 props。当你需要交互性时,你可以设置 state。
Challenge 1 of 3: 提取一个组件
这个 Gallery 组件包含两份个人资料,其中有一些非常相似的标记。从中提取一个 Profile 组件以减少重复。你需要选择要传递哪些 props。
import { getImageUrl } from './utils.js'; export default function Gallery() { return ( <div> <h1>Notable Scientists</h1> <section className="profile"> <h2>Maria Skłodowska-Curie</h2> <img className="avatar" src={getImageUrl('szV5sdG')} alt="Maria Skłodowska-Curie" width={70} height={70} /> <ul> <li> <b>Profession: </b> physicist and chemist </li> <li> <b>Awards: 4 </b> (Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Davy Medal, Matteucci Medal) </li> <li> <b>Discovered: </b> polonium (element) </li> </ul> </section> <section className="profile"> <h2>Katsuko Saruhashi</h2> <img className="avatar" src={getImageUrl('YfeOqp2')} alt="Katsuko Saruhashi" width={70} height={70} /> <ul> <li> <b>Profession: </b> geochemist </li> <li> <b>Awards: 2 </b> (Miyake Prize for geochemistry, Tanaka Prize) </li> <li> <b>Discovered: </b> a method for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater </li> </ul> </section> </div> ); }